- These lectures were
conducted during Semester at Sea, Winter, 2005,
by
Prof. Robert Fessler, Global Studies Coordinator. This section covers
the period from from Hong Kong to Chennai, India.
- Most of these notes were entered
in real time during the
lecture. Beware: I get things wrong.
- Personal comments are usually
enclosed in {...}
|
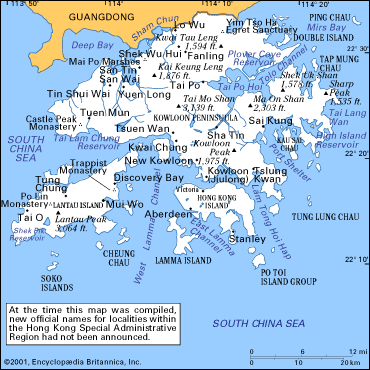
Hong Kong
 essler
began today by announcing that the next exam will be the day before
India.
essler
began today by announcing that the next exam will be the day before
India.
For the exam, students must be able to identify the countries on a
blank map of Africa.
Today: The East Asian world-view. Next Vietnam and Cambodia.
East Asia - Shared roots and culture
Religion - spread & modified
Vietnam has another version of Buddhism
VN has always been isolated by geography
Human habitation started in the North of VN with
ethnically Chinese people.
roughly AD 1000-1600 people moved south along the
South China Sea
"vietnam" in Chinese means "people in the south"
there were indigenous ethnic groups: chum, khmer
life was easier in the south than in China
so the people became more outwardly oriented
they were on the trade routes
more entreprenurial
there arose two cultures in VN:
North -traditional
South - laid back and outwardly oriented
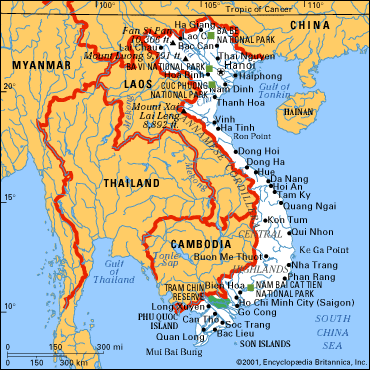
Vietnam
Dr. Penny Campbell - History of Vietnam
(4 sections: classical, French, Nationalism,
post-WWII )
1. Classical VN
immigration from China as early as 400 BCE
VN had three areas:
Tonkin in the north (name means "Red River")
Annam in the middle, (means "pacified south")
Cochin-China in the South and Mekong Delta (name
given by the French)
culture typified by water buffaloes, paddy rice, pictographic language
govenrment was on the model of the "Confucian emperor"
a man of wisdom
in harmony with a "cosmic plan"
examination system
bureaucracy
hierarchical
Gradual creation of a society based on that Chinese model
in Hue, Hanoi, etc. will see lots of Chinese architecture
pagodas
yin-yang roof (columns of nested "U" tiles
interleaved
with columns of nested inverted "U" tiles)
legal system based on that of the Chinese, but more lenient
daughters could inherit and manage property
the main threat to VN for most of the last millenium was Chinese
domination
in 939 AD they achieved independence from China
The incoming confucianism supplanted an existing "Hindu-ized Buddhism"
The ruler was the "Deva Rajah" or "god king"
a father figure to the country
eg: Sihanouk of Cambodia
2. The Coming of the French
{From another source, I understand that
the Pope allocated Indochina to the French. I don't think he asked the
inhabitants, but after all, they weren't Catholic.}
French were Roman Catholic
religion and commerce were intermixed, not separate
French also got Myanmar (then called Burma) and Thailand (then called
Siam)
French arrived in 17th century
French gov't then got involved in local VN politics
were called on to settle disputes
helped found the Nguyen dynasty
beginning with Gia Longe in 1802
Finally codified the whole as "French Indochina"
one colony: Cochin-China
under direct French rule
four protectorates: Annam, Tonkin, Cambodia, Laos
under local rule with some French
oversight
various progress from 1860 to 1890
in the 1860's, emperor Tu Duc was defeated by the French
he ceded the heart of Cochin-China to France
at that time, Siam was trying to control Cambodia/Laos
expanding eastward
King Norodom of Cambodia asked the French for help
The British were trading with China by going up the
Yangtze
France wanted to open trade routes into China along
the Melong River
{just their luck} the
river had too many rapids for trade}
in the 1870's, the British and French merchants in the far east got
into "quarrels"
the Chinese still held Tonkin
in the 1880's, France got Tonkin
Laos then signed a "treaty of friendship" with the
French
the "Indo-Chinese Union" was established in the 1890's
there was a governor and a "Residente Superiour"
{but which was who? and where?}
The French improved life and the infrastructure in Indochina.
Mostly with the
goal of more easily extracting wealth.
- centralization: defense, communication,
transportation, customs
regions handled local affairs, health,
education
- finance
colonies had to be self-supporting
France imposed all sorts of taxes
established more efficient collection
of taxes
gov't monopolies on opium, salt, alcohol
- public works
harbors, highways, bridges, telegraph,
swamp drainage
used conscripted labor
- economic development
French banks, F. mines, F. plantations
(coffee, tea, rubber)
locals were discouraged from creating
businesses
- created charming cities: Hanoi, Saigon
|
statistics
- much production of rice, rubber
- great improvement in public health:
life span increased, infant mortality
reduced
led to overpopulation and decreased std
of living
- wealth became concentrated in few hands
- Chinese began in-migration
Cholon was largest Chinese community
outside China
|
social philosophy
- abolished slavery and cruel punishments
- ostensible non-interference with religion
but missionaries were very active
- education
started with teaching French to a few
so they could have
interpreters, tax collectors, a "service" class
- worked toward universal education in
early 20th century
but only taught half a
million by WWII
- private schools did develop an upper
class
these were the foundations
of nationalism
(moral: don't educate people you want to subjugate)
- universities in both Saigon and Hanoi
|
World events began to impact Indochina
(& Africa & India
{&everybody else, too})
defeat of Russinas by the Japanese
demonstrated to Asians that Asians
could defeat Westerners
Russian Revolution - communism
Gandhi in India
in WWI France used some VN soldiers to fight in
Europe
they were thus exposed to the wonders
of the western world
and to its martial capabilities
Pan-African meeting was held in Paris
the Paris Peace Conference {what peace?}
Ho Chi Minh attended
3. Nationalism
after WWI
various political movements in VN
almost all had goal of ousting the French
Ho Chi Minh's party wanted the same
but also land reform and "economic
justice"
WWII
1937 Japanese attacked China from Manchuria
1940 Japan invaded Indochina
wanted rubber oil and rice as war
resources
Japan had a "friendship" treaty with Germany
the Vichy gov't in Indochina welcomed
the Japanese
Ho Chi Minh moved around
America
used Dec'l of Indep in his VN
declaration of indep from France
Paris Peace Conference
Vietnam
prison in China
mountains of VN
4. Post WWII
HCM had inclusive policies {toward what??}
1945 HCM emerged from the mountains
took over Hanoi and Tonkin
in the south of VN, Japanese surrendered to the
British
British gave VN back to the French
{first American death in VN: 1945}
1946 HCM returned to the mountains
1946-1953 saw the "First Indo-Chinese War"
by 1953 HCM's guerilla tactics succeeded (actually Gen. Giap)
France needed to rebuild internally from WWII
France was negotiating with HCM
but then came the utter defeat of the French at Dien
Bien Phu
valley north of Hanoi
French were surrounded by HCMs
army
{French commander assured his troops
that no one could mount cannon on the hills surrounding the fort. Giap
assured his troops that they could. He was right.}
(Note: If you have no class at
10:45, please avoid elevators.)
(Note: Short faculty meeting after class.)
Campbell: Vietnam, Cont'd
Yesterday got through Dien Bien Phu. We now go on from there.
1954 Geneva meetings on Laos, Cambodia, VN
VN "temporarily" divided
agreements made (soon ignored)
-- all foreigh troops to withdraw
-- no external arms providers
-- no foreign military bases
-- free trade and movement between N and S VN
-- national election to reunify VN
also 1954: founding of SEATO - Southeast Asian Treaty Organization
mutual defense
US, Pakistan, Phillipines, ...
S VN was a "protocol" country
to be protected it attacked
Paris {??Geneva} accords accepted by N VN, Laos, Cambodia
S VN rejected the accords
under leaders
Bao Dai - playboy ex-king
Diem - president
refused trade w/ N VN
this was silly since the two VNs
are symbiotic
N has resources and
industry
S has food,
especially rice
S VN relied on US for industrial goods
refused elections
(wisely so; the more populous N would
have prevailed)
S VN became a totalitarian & authoritarian state
50% of arable land in Mekong delta owned by 2.5% of
people
Diem Roman Catholic
his brother was bishop
intolerant of Buddhists
Bao Dai returned to play in France
Diem in charge
Diem dependent on US
US paid for S VN military
ditto 80% cost of gov't
ditto ports, harbors, airports, ...
Buddhists dissented
were ignored in US
some monks burned themselves
(In Hue you can see a blue car beyond a
pagoda. Monk rode in it to go burn himself)
US public did not understand
N VM also authoritarian under
HCM
nationalization of key sectors
communication, mining, ...
"mixed" economy (some planned, some capitalist)
private ownership of small operations
land redistributed to village ownership
suppression of dissidents
technical assistance from China, Russia
(& thus N VN was a "client" of
communist states)
war resumed in 1056
1960's
progressive infiltration of N into S VN
progressive dissaffection in S VN
by 1961 gov't had lost control of 80% of S VN
HCM established the National Liberation Front (NFL)
{where? who?}
platform of reforms
work to convince people of wrongness of S VN regime
early 60s, Kennedy
started the "Green Berets"
to be a guerilla force
started "strategic hamlets" policy in S VN
relocate loyal villagers to secure
places
{so loyalty "rewarded" with disruption}
very disruptive to the countryside
read Frances Fitzgerald "Fire in the
Lake"
a man refuses
to leave the home of his ancestors
no luck
everything failing due to corruption in Diem regime
by 1963 there were 15000 US "advisers" in S VN
akin to the Peace Corps {claims Campbell}
military personnel {says I}
involved in training and managing S VN
military units
1963
Kennedy assassinated
Diem assassinated (w/ US encouragement)
succession of generals ruled S VN
{We often hear of general ruling
a country. This is usually seen as a Bad Thing because they tend to be
authoritarian. However, in some situations the mlitary are the ONLY
group of organized people. Only they can communicate and coordinate
policies. Only they can organize even the most mundane civic tasks like
collecting the garbage. The other organized grouptends to be religious.
But their record is not especially better than that of military
governments.}
Lyndon Johnson saw a lack of success and his generals called for more
US power
Johnson escalated the war: sent more and more troops
{an illusory skirmish in the Tonkin
Gulf was interpreted as N VN firing on a US vessel. So Congress passed
the Tonkin Gulf Resolution giving Johnson all the slack he needed to
dive whole-hog into VN.}
US gave eqp't and ground troops to S VN
they conducted surrveillance and sabotage
futile - a bridge destroyed in Hanoi was replaced in
a single day
Why did the US get into S VN? {Excellent question!}
lots of theories
domino theory
alternative would be worse
unite US populace behind an effort
{hah!}
no first-rate power could refuse to
fight
many US leaders of the time claim in their memoirs
they had misgivings
1968 Jan 31: Tet offensive
80,000 N VN soldiers attacked targets throughout S VN
maybe half were killed
but was a termendous vistory for N VN
it demonstrated that a military victory
for S VN was unlikely
sharp escalation of protests in US
in the fall of 1968, Nixon was elected
"I have a secret plan to end the war"
Campbell actually admits voting for him on that basis
she now regrets her choice; she is bitter
Nixon, she thinks, dragged the war on for 4 more
years
so he could get re-elected
she thinks he was cynical and calculated {what
Nixon?!?! well, hardly ever}
more than half the US deaths in 'Nam came after
Nixon's first election
Nixon extended the war into Laos and Cambodia
US worked for the overthrow of Sihanouk
{because he would not let US
attack inside Cambodia}
paved the way for {the maniacal murderer} Pol Pot
Peace accord reached in 1973
N VN simply moved in in 1975
{map}
many gov't officials and collaborators moved to US
{and started manicure salons}
N VN regime undertook transformation of culture of S VN
remove "bugeosois legacy"
bars were closed
removed prostitutes, beggars {there were no clients,
anyway}
no books, newspapers
re-education of teachers and officials
religious buildings were "repurposed"
economic transformation
5 yr plans for agriculture and heavy industry
(especially needed to recover from
agent orange defoliation)
nationalization and collectivization
country was rebuilt in 70's and 80's
now
country has rapid, export-driven growth
VN does have resources:
food, fish, minerals, oil
half of GDP is agriculture
almost universal literacy
long life expectancy
lots of foreign investment
60% of population is under 30
the 1973 agreement called for diplomatic relations
did not happen until 1990's
good as things are, however, a visitor must remember
that leadership is still military and the communist
party
Fessler: Cambodia
Cambodia has yet another world-view
Hinduism
from India
let's follow history to see how Hinduism got to
Cambodia
as recently as 4000BCE, Cambodia underwater
area is mostly flat; silt deposited by the Mekong
houses were often built on stilts
diet of fish and rice
about 1000BCE, trading settlements grew up
Khmer among them
waystations on India<->China routes
ships brought Buddhism and Hinduism
gradually religions spread, especially Hinduism
{? 800 BCE}
Jayarvarman II made a series of conquests
unified the settlements into a kingdom
the kingdom of Angkor
long succession of Deva Rajahs ruled
hierarchical social structure
Hindu-based
station based on birth, not examination
ruling power descended from god Shiva
Shiva lives on Mt. Meru {where is it?}
Jayarvarman built a temple symbolizing Mt. Meru
each succeeding deva rajah built a new temple
same basic pattern
Jayarvarman {or somebody} built irrigation systems
Suyavarman II 1112-1152 CE
worshipped Vishnu rather than Shiva
expanded the Angkor empire
Malaysia, Cochin-China
built Angkor Wat
Jayarvarman VII
Buddhist (unlike predecessors)
built Buddhist temples and revised others
Angkor Thom; Ta Prohm (now overgrown by jungle)
in 1400's {? tourguide says 1443 for abandon Siem Reap}
empire in decline
irrigation silted up
attack from E and W
temples abandoned
moved to Phnom Penh
weaker and weaker kings
in 1600's king agreed w/ VN
ceded Cochin-China to VN (was "lower Cambodia")
1953 - independence for Cambodia
Prince Sihanouk tried to remain neutral in VN war
by 1965 he feared US wanted to supplant him
so he sided ith N VN
allowed VC to build bases in Cambodia
1970 Sihanouk visited Paris
overthrown by Lon Nol (w/ US approval)
Lon Nol gave US permission to bomb along VN border
Sihanouk supported a small revolutionary group
called Khmer Rouge
under Pol Pot
guerilla war 1970-1975
1975 Lon Nol fled the country
Khmer Rouge radically restructured Cambodia
one flight to Biejing every other week
no other outside communication
Pol Pot wanted a Maoist agrarian society
most non-peasants were executed
then KR began infighting and executing each other
deaths - between two and three million
20-33 % of population
outside world did nothing
finally in 1978, VN invaded Cambodia
in two weeks they drove the KR back
into the jungle
guerilla war for 20 more years
more land mines in Cambodia than anywhere else in the world
avoid getting off the travelled areas
Country is highly unstable
government is factionalized
there is, for the moment, peace
Fessler
says traffic in Vietnam pales in comparison to India.
Starting now on India.
But first:
Islam.
Because India has the 2nd largest population of
Moslims.
And because we will be passing the largest population: Indonesia
Islam is the worlds newest and fastest growing major religion.
Started w/ Mohammed in Mecca, 610 CE
Revelations from Allah. Basis of Qu'ran.
20 years, most of middle east
40 years NAfrica, Spain
by 700 AD Islamic empire spanned from Spain to China and North to the
Himalayas
Islam - means Peace, Surrender to the word of Allah
Moslim - follower of Islam
Qu'ran - holy book of Islam. Revelations from Allah to Mohammed
Hadith - another sacred work in Islam. All works of Mohammed
other than Qu'ran
Sharia - literally "the well worn path to the watering place," denotes
Islamic law.
established by interpreting
Qu'ran
interpretation needed because Qu'ran written in 610
Catholicism is hierarchical
Islam is not so.
Hence Sharia varies between localities based on
local scholarship.
Woman's dress: Qu'ran says "modestly"
Taliban: very strict
Egypt: scarf and long sleeves
Monotheistic religion - one God
goal - a single human community united in following
Qu'ran
Jihad - "holy war"
"greater jihad" - the war between good and eveil
within oneself
"lesser jihad" - war in defense of Muslim community
Jihad can only be declared by learned scholars.
And therefore locality specific.
Muslims in that area must folow
five pillars of Islam - beliefs
Shahada - faith and belief in in Allah and in Mohammed as his final
prophet
Salat - prayers five times a day, facing Mecca
direct link from worshipper to Allah
Zakat - Charity, giving to the needy
Sawm - self purification through fasting
during month of Ramadan -no food, drink, sex during
day
Hadj - pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in lifetime
if physically and financially capable
Isalm is guide for all of life
Sharia covers everything. Examples
Do not eat pork
Do not drink alcohol
Cannot earn interest
Blasphemy punishable by death
insult either Allah or
Mohammed
Adultery puhishable by death: both man
and woman
evidence needed -
pregnancy enough for woman
for a
man, evidence is four witnesses
polygamy
man may have multiple wives
man must treat each wife equally
woman must not have multiple husbands
varies by country
divorce
man says "I divorce you" three times (over three
months)
not while woman menstruating (early reaction to PMS)
woman can get divorce by getting a judge to give her
one
men outrrank women within family
important to keep family
woman can hold important posts
such as prime minister
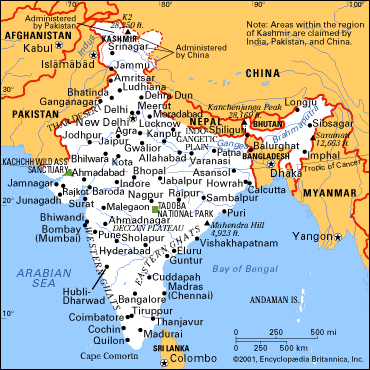
India
incredibly diverse
young country (1947)
very old culture (3000 BCE)
both a modern and traditional society
nuclear power
most number of scientists
internet and satellite dishes everywhere
But
50% literacy
...
35% poverty
Calcutta 700,000 live in streets
middle class similar to US
10% incredibly wealthy
Language
324 distinct spoken languages
no one language spoken by more than 40% of population
18 official languages
English is a common language, but not
offiical
area 1/3 that of US
unified, but diverse society
religion
85% hindu
14% muslim
2% christian, buddhism, sikhs ...
local areas may have other majorities
Punjab: Sihks
source of divesirty
100 million years ago
India attached to East Africa
tectonic plate moved
28 million years ago, smash into Asia
pushed up the Tibetan plateau by 3 miles (5 kn)
raised the Himalayas
they are still rising
geographic isolation for India
mountains to the North, the sea all other sides
some passes
eg Khyber Pass
difficult for people to move into India
prevent easy interaction with outside world
within the Indian subcontinent there are other barriers
N. India dominated by 3 rivers and therefore fertile
Indus
Ganges
Brahmaputra
Indus - 2000 flows SW in Pakistan
Sanskrit word for river is "Sindu"
Persian pronounciation is "Indu"
and they called the people on the other
side "India"
Greeks and Romans called it "Hindustan"
locals called it Bharatha
Indus joined by five others to make "Punjab"
Ganges
flows S and then E and
joins Brahaputra
thru Bangladesh
worhippsed as a goddess
Allahabad
where Umana river joins
the Ganges
third river there is the
invisible Sarawati
bathing there Mahacoom (30
million in 2001)
right time is once every
12 years
Varanasi
most scared Hindu city
oldest inhabited city in
the world
dying there means you can be released
from reincarnation
funeral pyres day and night all along
the banks
Brahmaputra - "son of Brahma"
(330 mill. gods and goddesses in Hindu)
East South West
Ganges and Brahmaputra make a big circle
sacred area within
There are other rivers in the South, but they are sporadic
Most of India gets no rain.
Except for monsoons. Somewhere between June and November
Southern India depends on Monsoons./
Land heats faster than ocean.
air heats and rises.
brings in wet ocean air
it rains
cyclical monsoons are part of the Hindu belief of reincarnation
patchwork of settlements
becaue people settled where there was fertile land
each isolated group developed their own
languages
religions
customs
no movement ever swept across India
Hinduism absorbed local beliefs as it spread
Where did it start?
First major civilization in Indu valey
3000 BCE to 1500 BCE
Harradan or Indus Valley civilization
cities up to 50000 people
brick buildings, all bricks same size
gridded layout
alleys half the widths of roads
highways twice the size of the roads
indoor plumbing
language and written works
believed to have been a matriarchical society
event of 1500 BCE: unknown.
Indus Valley Civilization vanished
civilization spread over 1000 or more miles
after 1500 BCE, some people went South
Darvidians may be descendants of Indus Valley Civ
others spread across N India
small frming settlements
roughly 1500 BCE Aryans arrived through Khyber pass
not an invasion, more like a meandering
probably several migrations
conquered the farmers
no written language
spoken language was Sanskrit
the first mixing of belief systems
the beginning of Hinduism
2nd Global Studies exam the day before arrival in India.
need to know African countries
Becky Drury introduced the new
captain. He was with Pearl Cruises for 7 years and is now working for
Raddison cruises. Home in South of France. Wife in Ukraine studying
Captain Jeremy Kingston: Welcome back. "Name too long for a tee-shirt,
so I'll try to keep the voyage smooth."
Fessler: today Hinduism and the caste
system
First civilization Indus Valley Civilization 3000 BCE - 1500 BCE
Aryans arrived through Khyber pass: pastoral warriors.
they rode horses
had chariots, wagons, herds of cattle
quickly dominated northern India
Hinduism is a mixture of belief indigenous and Aryan beliefs
Aryans had animistic belief system: tree, sky, sun, ...
Can appeal to specific spirit for help in specific areas: health,
battle, crop, ...
Make offerings and sacrifices.
sacrifice involves spilling of blood
Suppose do ritual and fail to get result
One explanation: failed to do ritual right
Became obsessive
rituals got larger
community rituals with many sacrifices
precise placement of altar
early studies in astronomy
early studies in anatomy
priest class arose
keepers of the sacred knowledge - how to do rituals
"right"
lasted for a millenium
no written language
so had to memorize instructions for huge rituals
long verses of poetry: order, intonation, ...
10-20 thousand verses
generation after generation
Aryan social structure
many tribes of Aryans
ea. w/ only chief ("Rajah")
those related to rajah were in the ksatriya
(see also Moses and his
relatives Levites)
ksatriya - rulers and warriors
below are priests: brahmins
next: producers -- farmers, potters -- vaisya
next: non-aryan, local indigenous -- servants -- sudra
eventually became settled
land was fertile, no need to move
importance of brahmins and ksatriya swapped
now: brahmins, ksatriya, vaisya, sudra
verses became the four categories of "vedas"
each category a differnet group of Brahmins
concepts:
atman - "soul" subtle essence existing in body
brahman - "power in the universe" "essence"
three levels of existence
earth
atmosphere
heavenish place where gods
lived
believed the three levels of universe must be in harmony
order and predictability
to maintain harmony
speak truth
perform duties correctly
or else you threaten the harmony of the universe
dharma -ordering principle in the universe - harmony
need to follow your dharma to maintina order in universe
around 700 BCE, written language
wrote down vedas
began to write also: sutras
discusssion, threads
written by brahmins (the only literate people)
dharma sutra
written discussion of proper behavior for your place
in society
so brahmins became determiners of proper behavior
Laws of Manu (by Manu), a dharma sutra
detailed manual for correct moral behavior
gave a religious basis to the custom of putting people in classes
existence was part of harmony of universe
hereditary
division stemmed back to creation
creation myth
huge giant chopped into pieces
head - brahmins
arms - ksatriya
legs - vaisha
feet - sudras
classes called "varnas"
word "caste" is a much later Portugese word
Manu said further that there was a fifth group
deallt with death or filth
undertakers, tanners, buthcers,
outside the caste system
"outcasts"
Manu assigned specific social duties to a class
cannot marry outside varna
cannot accept food from caste below
Brahmin cannot be touched by and outcast
outcasts became known as untouchables
had to live downwind
wear bells to swignal approach
a heirarchy of purity
now back to local people and their beliefs
social structure according to occupation
jati - (jah tee)
hereditary - born into occupation
aryans plugged the jati into the varnas
?stuck in caste
not quite true
a jati can move relative to other jatis within a
single varna
jati is extended kinship group
context for sociql interactions
expected to marry within jati
determine who you can eat with, color of house
In India, caste system is illegal
But you cannot legislate against age old behavior,
especially that deescribe in a religious context
hundreds of millions in India do not believe in caste system
but much of India is very local
majority of people follow caste system
untouchables have other names
harijans (named by Gandhi) "God's children"
dalits "the oppressed"
Hinduism is more the Manu, it is a living religion
30 million gods
themes of Hinduism study
#reincarnation
motivation for remaining in lowest classes?
various sutras mentioned multiple lives
you can reincarnate in higher or lower caste
karma determines future caste
karma is related to dharma
if you follow your dharma,
you accumulate good karma
and vice versa
good karma aids in health, fortune, ...
good karma means you may move up in
caste
it is assumed all people have a long past history
your best opportunity to improve next time around is
your current caste
dangerous to try to live a higher caste: you will
fail and come out lower
also no point in helping a lower caste person,
it may damage there attempt to
live up to dharma
avoids middle class guilt
as time went on ...
Aryans having communal rituals
around 500 BCE
sects opposed to sacrifices
Jainism
Buddhism
Brahmins became concerned about population losses
Sutras began to consider alternatives to big ritual sacrifices
Induce gods to visit earth and stay
Artist create an image
Brahmin might induce a god to inhabit
that object
Individual worship arose
Decentralization
puja -"prayer", but doable individually
different Hindus gravitate to different gods or godesses
brahmins threatened with loss of position
so brahmins began to say: maybe not the rituals
maybe it was something having to do with Brahmins
postulate that they had altered consciousness
so they tried to see how to develop
Upanishads - "secret teachings"
collective wisdom of priests
intended for those with special abilities
now saying gods powerless, but have power from theri
brahaman
now seen that people themselves could get brahaman
within themselves
moksha -libertaion - no more rebirht
nirvana - buddhist word for same thing
brahmins said that ordinary consciouness is confused
two selves
jiva - self caught up in sensory world, physical,
subject to illness, pain, ...
separate from other people
preoccupied with thoughts
about "me", "I"
pursues physical
pleasures, wealth, material things
atman - soul
uninvolved, non-physical
observing self
not subject to pain,
illness, ...
all objects are created by
senses
and therefore illusory
the doctrine of maya - the world is an illusion
brahmins say people need training to recognize the two selves
to get in touch with atman
must do discipline to get in toiuch
meditation, yoga, ...
focus attention on atman
reach a state of detachment from material world
transformation
goal of yoga is to separate atman and jiva
and shift to atman
achieve moksha - liberation
upanishad describe four stages of life for upper caste men
different dharma per stage
1 student - study
2 householder - married, children,
career
3 forest dweller - after birth of first
grandson
4 sanyasin - walk off and never look
back. abandon possessions. cut all ties
wandering
beggar. begging bowl. one piece of clothing
no concern
for body; it is an illusion
no desires,
hopes, regrets, ...
achieve
moksha - no more reincarnation
Fessler: Introduce interport
lecturer and students.
We have covered:
Hinduism and Caste System
context for present day India
selective history: root of what we will see
more history
Northern India at that time (~327 BCE) a whole series of
kingdoms. Not a country.
327 BCE Alexander the Great
at the Khyber Pass
(ended with largest empire ever seen to that time)
swept through N. Pakistan
huge battles with elephants
ready to cross the Indus
soldiers got tired and wanted to go home
fought South along the Indus and sailed across Arabian Sea
left a power vacuum
in moved Chandra Gupta
built empire all across N. India
began Mauryan Empire
left to Gupta's son and grandson Asoka
Asoka (ash-oh-ka)
268-233 BCE
great leader
all acroos N. India
as far South as present day Chennai
first unified empire
about 8 years after assuming office
100,000 enemies killed
Asoka remorseful
vowed to not fight
converted to Buddhism
declared Dharma to be the way of the
empire
dharma in Buddhism is a little different
not hierarchical, no position in castes
dharma same for all
your dharma is to behave in a mindful and
compassionate way
Asoka made many changes
animal sacrifices forbidden
meat eating discouraged
vegetarianism encouraged
religious freedom
justice system
planted shade trees
bug wells
rest houses
also responsible for expanding Buddhism from small sect to major
religion
established monasteries
encouraged spread across Asia: China, Thailand,
Japan, ...
on Asoka's death the empire unravelled
partly due to Hindu Brahmins wanting to preserve
power
roots of tension between muslims and hindus
why broken into India and Pakistan
why dispute over Kashmir
skip forward to 700 AD
Islam to the west of khyber pass
Hindu to the east
pause in spread of Islam
Hindus learned about Islam
Small Muslim communities in the S India
~1000AD
Mahmud, a muslim, began a series of raids through the Khyber pass into
N. India
loot
demolish Hindu temples
(to get the gold and jewels)
convert "infidels"
or kill them if they wouldn't convert
after each raid, retreat back across the Khyber
1190 Prithviraj ruled kingdom around Dehli
about half of the Punjab
Mohammed of Ghor had the other half of the Punjab
(boundary close to boundary India -
Pakistan
Prithviraj suggested a truce
Hindus celebrated
Mohammed slaughtered 120,000 Hindus
Now Islamic forces worked their way across India
looted and destroyed Hindu temples
they stayed
built Mosques on top of temples
established Islamic Sultanates
demanded conversion to Islam
1222 AD: Gengis Khan and Monguls came from central Asia
Monguls conquering China and Japan
Moguls thru Khyber pass
passed wave of Moslems ahead of them
moslems stayed in N. India
N. India became Islamic
many Hindus converted
some killed, other not
more about Islam
"there is no god but Allah
and Mohammed is his final prophet"
earlier prophets
Jesus, Moses, ...
but earlier word contaminated by time
and translation
so Mohammed is the true word of god
so Islam is extremely accepting of Jews and Christians
called "people of the book"
allowed religious freedom
accepting of monotheistic religions
as long as not a threat to Islam
missionaries are one sort of threat
Jizya (giz-yah) - tax paid to worship freely
back to N. India
Islam vis a vis Hinduism
Hinduism has lots of gods and goddesses (330 mil.)
but others argue that the gods are all aspects of one god
Hindus less modestly dressed
horrifying
Hindu temples covered in sculptures
some even depicting sex
Moslem mosques have no pictures
so some moslems horrified
Hindus can worship individually
Islam worships in community, 5 time a day
Hindus: hierarchy
Islam: equality
Hindus: pork but not beef
Islam: beef, but not pork
nonetheless, Islam and Hindu lived together for a long time in N. India
Hindus adopted more covering
Islamic mystics attracted some worshippers
and in S. India co-existence continued
--> early 1500s AD
Afghanistan ruled by Babur
a descendant of Genghis Khan
is a Muslim
Lodi ruled area around ---
Lodi wanted help to expand
Lodi 120,000 soldiewrs, 1500 elephants; poorly trained
Babur had 1/10 soldiers, but had trainiing and guns
Babur cirlced Delhi and awaited attack
Babur easliy won
marched across India to NE India
Mughal Empire
ruled for three centuries
Babur succeeded by son Humayun
Humayun shared power with brothers
empire split
Humayaun too busy with women and opium
son Akbar succeeded Humayun
took control at age 13
dyslexis, but brilliant soldier
had been born in India
so he did not see Hindus as barbarians,
but as fellows
repealed the Jizya
celebrated Hindu festivals
married a Hindu (daughter of a rajah)
bigger empire than Babur
learned from fathers mistakes
did not share power
abolished Islam as the state religion
remained a Muslim, but tolerated other religions
roads economy improved
supported artists musicians. huge library
1605 - Akbar dying
son Jahangir proclaimed himself the new emperor
Akbar sent lieutenant, Jahangir killed lt.
Jahangir took over
scholar, not a fighter
married a muslim (after killing her husband)
wife made most of the decisions
strengthened Moslem presence
schemed to have her son
take over
as Jahangir dying, sons squabbled
Shah Jahan won out, killing the others
dismisssed the Moslims his mother had put in place
built new city on city of Delhi
built Taj Mahal
wife dies giving birth to 14th child
1657 Jahan died
four sons squabbled again
oldest was Sufi and governor of Punjab
disliked by the others
second son a shiite (?)
third son a drunk
aurangzeb, fourth son of Shah Jahan
soldier and therefore acceptable
imprisoned his father across the river
from the Taj Mahal
ruled 1658-1707
Arangzeb captured oldest brother
dragged thru streets of Delhi
wrapped head, delivered to father
2nd brother ran off to Myanamar
3rd brother was tricked, imprisoned, executed
Arungzeb was strict Sunni Muslim
prohibited repair of Hindu temples
banned alcohol, music dance
Hindu govt workers replaced with muslims
temples replaced with mosques
appointed "morality police"
reimposed Jizya
protests and revolts increased
religious co-existence started to unravel
Mughul Empire continued for 150 years (til, say,
1850s)
gradually unravelled
religious hostility remained
Fessler Announcements:
--video at 6PM and 7 PM
documentary on untouchables "Lesser Humans"
born to clean outhouses
--second global studies day after tomorrow
India
Last major outside influence: Europeans
about the time of the Moghul empire
Europeans wanted the spices from India
eg, pepper worth more than its weight in gold
wanted sea route to India
avoid the Middle Eastern middlemen
shortly after Columbus, (16th century)
Vasco de Gama found the sea route to India (1498)
bargained for little pieces of land
Goa (Portuguese)
Pondicherry (French)
gold from Europe for spices from India
1600 - British wanted in on spice trade
QE I granted charter to 25 business men in London
monopoly between all trade
between England and Britain
pay annual fee to Britain
British East India Company
BrEIndia Co got unwanted land
Bombay, Calcutta, Madras
set up trading posts
spices, then textiles (mostly cotton)
hired local Indians as workers, guards, etc.
Seepoys - security police
-well- trained by British
became a private company army
Portuguese tried to bring missionaries
bad move
so BEIC banned missionaries
BEIC kowtowed to local emperor, gave bribes as needed
were seeking "farman"
"imperial directive" from the emporer
to get sole access: eliminate other Europeans
when Aranzed died successors were weak
independent local officials arose
fragmented into little kingdoms
BEIC would back a local official
and back him with Seepoys
give him a "company adviser"
lots of puppet kingdoms controlled by BEIC
1716 - finally got farman
emperor weak
BEIC threatened to withdraw
additional provision:
BEIC had right to take action against
infringement on edict
over the years BEIC gained control of increasing territory
sometimes needed full fledged wars
Seepoys (Indians) vs. other Indians
British gov't continually raised the cost of the BEIC monopoly
so BEIC branched out to trade with other countries
eg, southeast Asia
BEIC people getting extraordinarily wealthy
eg. Elijah Yale
1813 - Br. parliament ended BEIC charter
other Br. merchants now allowed to compete
other companies brought missionaries
few Hindus or Muslims converted to Christianity
missionaries set up schools
many Indians were taught in English
the various Br companies put in mail, telegraph, railroad
45000 miles of RR tracks
inadvertently provided infrastructure for India
help to unify the country
meanwhile,
Indian people still divided: religion, locality
could not unify
British just kept on rolling
Sikhs, Gurhkas, Kashmir, ...
by 1850s abandoned puppetry
just put in company officials as rulers
1857 - BEIC mistake
new and more efficient rifles for Seepoys
need greased cartridges
had to bite off the end
rumors arose {HOW?}
Hindus: grease from cows
Muslims: grease from pigs
revolt - "The Mutiny"
turned on the British
British gov't decided to come to the rescue of Brit citizens
sent in British army
year long bloody war
British won
price to companies:
1858 - British gov'f compnay assumed control of BEIC territories
QV named empress
British colony
dismantled the DEIC
Prof. Penny Campbell - more on the British
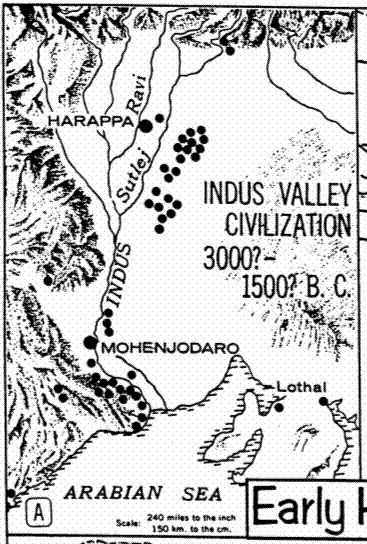
--Indus Valley Civilization
various cities up and down Indus valley
excavations started in 1920s and are ongoing |
 |
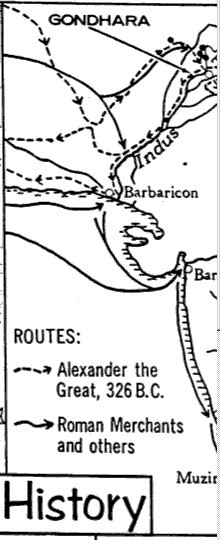
--route of Alexander the Great
Tixila, Buddhist Monasteries |
 |
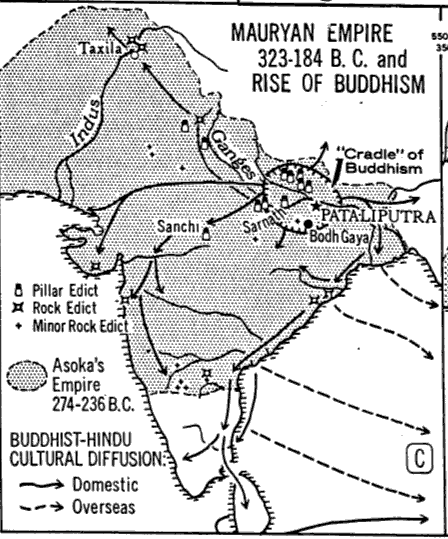
-- Maryan empire -
rise of Buddhism
Buddha's home is in S. Nepal
(300BCE) |
|
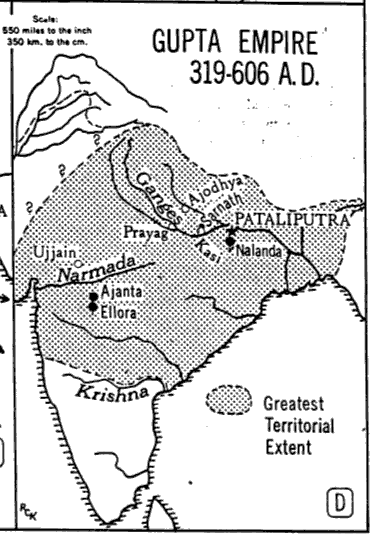
--Gupta Empire (300 AD)
lasted 300 years
Jonta caves, Buddhist retreats
Allaura sculpture of several religions |
|
{Historical maps of India}
(more maps on screen)
Spread of Islam into India
from 1190 - ~1500
Muslim empires in N. India
"Delhi Sultanates"
there was even a women sultan
(next one was Bhutto)
after conquest of aronxed, moghuls had greatest extent (1707)
(third map)
1790, 1835, 1860
1790 is almost two hundred years of BEIC
mostly just a chunk in the
northeast of India
1835 BEIC has advanced everywhere
especially up the Ganges River
good place
for growing Opium
and along southern slopes of Himalayas
1860 British Raj
majority of India
(fourth)
Princely States
1858 BEIC gave Brtain only 60% of India
40% divided among various
princes
(no more maps)
Post-Mutiny Changes in India
"high-noon" of colonialism in India
--internal boundaries became fixed
Br gov't said they would no longer grab territory
previously "doctrine of lapse"
death of prince without
heir meant that territory went to Britain
Br had treaties with 500 princes
and Br sent "advisors"
(Prince were just head of state)
--communication better - Suez, telegraph cables
Sec'y of State for India in London
Viceroy in India carried out direction from Sec'y
State
-- army remodeled
Crimean war had siphoned off British soldiers from INdia
(led to Mutiny)
so Britain increased ratio of British
Martial classes Gurkas, Sikhs, Pathans (puh tahns)
these were encouraged to join Br army in India
families encouraged to come from Britain
increase in number of civilian administrators
-- new attitude about India
Indians were distrusted by Brits
developed "cantonments"
area where Brits lived
Anglican Church, pub,
cricket, ...
-- bureaucratic administration
in 1833 civil servcie had become open for Indians
but to take exam, had to go to London
could only take exam once (age 22 or so)
1850s universities established in India
lowered age to take the exam
1859 - 22 1866 - 19
even in 1939 55% of Indian civil service were Brits
still 40% at the time of independence
-- goals of gov't change in latter part of 19th century
wanted profit
in 1860s few Indians were asked for input
councils were established
first census in 1872
Hindus, Muslims, Depressed classes
as Brits enlarged participation by Indians
based seats on quotas from
each religion
"communal basis" for
participation
became a curse
--export business
indians became affected by word markets
--raw materials
RRs built to get raw materials to ports
proponents of RRs claimed they would encourage local
industry
instead they stifled local development
population growth due to improved health
--economic development last part of 19th century
Br needed India to help finance world-wide trade
Br had a trade deficit w/ US
due to protectionism
Br could get trade surplusses in India
to finance deficits with
other parts of world
pensions had to be paid: widows, retirees
had to pay the interest on the RR bonds
summary
high point of Raj: 1858-1940
Br looked at India as case of long "trusteeship"
Br wanted to keep India ("the jewel in the crown" of
empire)
there was no "India"
loyalties to family, jati, local
community, ...
no sense of country
creation of Indian National Congress
founded in 1880s
few members initially
educated people from urban centers
was loyal to Britain
sang "God Save the Queen"
at annual meeting
among goals:
effort to abolish poverty
more Indians in civili service
exams in India
reduced military expenditure
more spnding on social programs
Lord Kurzon 1905 Calcuttta
decided Bengal too large
to administer
"partition of Bengal"
now border of Bangladesh
partition angered Indians
drive for swaraj - self rule
founding of Muslim league in 1906
felt that National Congress Party was
too Hindu
Thus two national parties, one Hindu & one Muslim
(picture of Ganhdi spinning cotton yarn)
Fessler:
(2nd exam tomorrow, bring a #2 pencil)
(Fessler will be on deck 6 all
day)
Read the following chapters in Port-to-Port:
China, Hong Kong, Vietnam, Cambodia, India
and these articles in Global Issues:
Articles 7, 12, 13, 19, 24, 25,
28, 31, 35,
37
Be able to identify the capital, form of
government, the head of state and the head of government for: India,
Kenya, Tanzania,
S.Africa
The correct names for current leadership of India are:
Head of State: President
Abdul Kala
Head of Government:
Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
Prof. Annakutty Findeis
{these notes incorporate the
slides used in the talk
my notes are in times-roman
font}
Contemporary Relevance of Mahatma Gandhi
Annakutty
Findeis
for Semester at Sea Global Studies
---
Many
Gandhis,
but only one MAHATMA GANDHI
Maha + atma =
great + soul
not related to any other noted Gandhi
(cannot buy "mahatma" with money)
--
GANDHI‘S
LIFE
Mohandas
Karamchand Gandhi (02.10.1869 – 30.01.1948)
Marriage 1883 (both 13 years old)
Studies in London 1888/91
Journey to South Africa 1893
1st African Experience 1893/99 Apartheid
– Experience of being an outcast
among the whites
Representative for Indian interest
--
What
sort of relations?
"The different
races of mankind are like different branches of a tree – once we
recognize the common parent stock from which we are sprung, we realize
the basic unity of the human family, and there is no room left for
enemies and unhealthy competition."
--
2nd
African Experience 1902/15
Satyagraha
Movement 1906
Satya = truth
Agraha = firmness
--
DEDICATION
TO INDIA
Return to India
1915
Leading the
struggle for Indian Independence (-1947)
--
Maxims
for freedom movement
- Satyagraha – firmness of being in the truth
- Ahimsa – not to hurt – non-violence (from Jainism)
- Swaraj – self-governance
- swadeshi – from one‘s own country, indigenous
(admonished Indians
to not use imports)
|
--
Removal
of Untouchability 1
"Every Hindu
should make common cause with Harijans and befriend them in their awful
isolation."
Gandhian ashrams membership required
vow for removal of untouchability
--
Removal
of Untouchability 2
"Removal of
untouchability means love for, and service of, the whole world, and
thus merges into ahimsa. Removal of
untouchability spells the breaking down of barriers between man and
man, and between the various orders of Being."
--
Removal
of untouchability 3
"We
find such barriers erected everywhere in the world..."
--
Ahimsa
"A person who
believes in non-violence believes in a living God. He cannot accept
defeat. Therefore, my advice is non-violence all the time, but
non-violence of the brave,not of the coward."
--
Mahatma
Gandhi
Father
of the Nation
Martyr
of Ahimsa
Assassination
30th January 1948 on the prayer ground
By Nathuram
Godse
In USA, MLK, Jr. was also a non-violent
victim of violence
{See also movie, "Pay it Forward"}
--
Gandhi
and America
Gandhi's
reactions to letters from America
"I do want to
think in terms of the whole world. My patriotism includes the good of
mankind in general. Therefore my service of India includes the service
of humanity." (17.9.1925)
--
BASIC
PRINCIPLES OF GANDHI‘S THOUGHTS
- Satyagraha (love and firmness)
active
resistance
to establish
justice and truth
satya =
sat (being) + ya (??))
- Ahimsa
(truth
and non-violence)
- Dharma
|
Gandhi‘s
understanding of
- religion and politics,
- society and economy
|
--
Holistic
Philosophy of LIFE
Spirituality and experience
Life as applied spirituality
truth is splendor of reality
need to understand the fundamental laws of nature
is dharma
Holistic Philiosophy of life
Spiritual and experience
Life accepted as spirituality
--
Holistic
Philosophy includes
Religion,
Politics, Society, Economy
All life-forms
and the environment
seeks dharma in field of politics
do good on largest scale possibile
god is truth, but Gandhi says truth is God
non-dual relation between religion and politics
promoted equality and socialism
cared for the weak
--
Sources
of inspiration:
Vishnavism
Bhagavad-gita
Upanishads
Bhagavata-purana, Ramayana
Jainism, Buddhism
New Testament - Sermon on the
Mount
Christian Humanism
Tolstoi, Ruskin
Qur‘an, Islam (from his childhood)
scriptures of all religions used in
Gandhi ashram
--
Relevance
of Gandhian Thoughts in the Context of Globalisation
Unity of the world – Unity of humanity with respect for diversity
Unity of thought and action
give respect to differences
plurality with equality
sarva dharma sama bhava
all religions equal concern
--
Relevance
of Gandhian Thoughts 2
Equality – social, religious, cultural,
national, international
Non-hegemonial partnership
Respect for nature
equality of cultures and nations
without subjugation
international relations
man should live in harmony with nature
--
ALTERNATIVE
PERSPECTIVES
Simple Life-style – Ashram-life
Respect and love for all forms of Life
Anti-consumerism
Anti-mechanism
Non-absolutism
Non-exclusivism
truth is not the property of any
particular religion
--
Satyagraha: Model of socio-political
conflict managment
Communicative method of negotiation
Rational compromise through reasoning and dialogue
Adoption of direct action techniques of satyagraha in case of failure
fasting, strikes,
Acceptance of suffering
{aye, therein lies the rub; many are
unwilling to suffer}
--
Gandhi‘s Vision of Civilization
"Civilization in
the real sense of the term consists not in the multiplication but in
the deliberate and voluntary reduction of wants. This alone promotes
real happiness and contentment, and increases the capacity for service."
--
Invitation to read
M.K. Gandhi, An Autobiography or The Story of my
experiment with Truth, Ahmedabad 1927
Louis Fischer, Mahatma Gandhi. His Life & Times,
London 1951
Selected Works of Mahatma Gandhi. V
volumes, Ahmedabad 1968
Fessler:
Gandhi also had a sense of humor. When asked what he thought of western
civilization, Gandhi replied: "I think it would be a good idea"
{Christianity is also a good idea,
though seldom tried by Christians.}
Prof. Penny Campbell
Partition map, 1947
all 500+ princes were supposed to join one country
or the other
Hyderabad held out (wanted Pakistan)
Map of Kashmir
Hindu ruler, Muslim population
ruler joined India
but Pakistani forces moved into part of Kashmir
Inidan gov't wants to retain partly because of
strategic location
1947 - 350 mil people
80% illiterate, in remote villages
enormous refuge problem
Hindus from Pakistan
Muslims to Pakistan
integration of 500 princeships was a problem
needed to expand civili service with Indians
still 40% British
needed constitution
1950
solcial economic and political justice for all
citizens
liberty of belief
no discrimination by caste
fraternity among citizens
secular, democratic republic
today: 3 areas: politics, economy, unity
1. Politics
National Congress Party dominated from the start
Nehru ruled for 17 years, til 1964
Westmoreland System
(british parliamentary model)
ceremonial head of state
prime minister
political parties chose symbols
because of illiteracy
also established federal system
national gov't: currency, defense, atomic energy
state gov't: education, health, agriculture
1964 Shastri
1965 Indira Gandhi
strong mind and fist
ruled in imperial style
17 years (minus 3 years)
Amritsar - Sikhs
holy center
fundamentalists for Punjab wanted autonomy
early 84, sent army into golden temple in amritsar
killed thousands
Sikhs retaliated by assissinating her
Sikh guards she insisted on keeping
(Penny recalled seeing marks on pavement a year
later)
PM Rajiv Gandhi 1985-1989
Indira's son
now party fragmented and Rajiv unable to reassemble
1990-2004: weak coalition gov'ts
eg, BJP - Hindu nationalist party
2004 Congress party came back under Sonya Gandhi (Rajiv's wife)
she was Italian
refused the PM-ship
Mr Singh is in power
aiadmk - political party
leader corpulent former movie star
jayalalitha - large, colorful woman
convicted of corruption thrice
leader in Tamil Nadu
2. Economics
Nehru wanted a socialist state
but no expropriation of wealth redistribution
wanted social justice
N believed in central planning
succession of five year plans
often called for increasing grain
production
sometimes emphasized steel and
electricity production
however, mixed economy
gov't control of only some industries
Indira nationalized the banks
tried to do land reform
commonly circumvented
Rajiv replaced socialist talk w/ offer to rapidly modernize
could bring in technology goods: TV, computers, ...
India has emerged as a technologically advanced
society
3. unity
National Congress party sought a secular society
communalism to be abolished
but there has been violent secularism
eg, after Indira assassinated, riots throughout India
Sikhs murdered
Yoda site has been an issue
Hindu temple replaced with mosque
nationalism
reject notion that politics is a-religious
BJP - right-wing Hindu nationalist thought
summary: for nearly 60 yrs
Nat Cong has ruled for 70% of time
mostly under Nehru's family
but still a democracy
moved from village culture to technology
there is still a great need for someone like Gandhi to come forward
to lead to respect for others and others religions